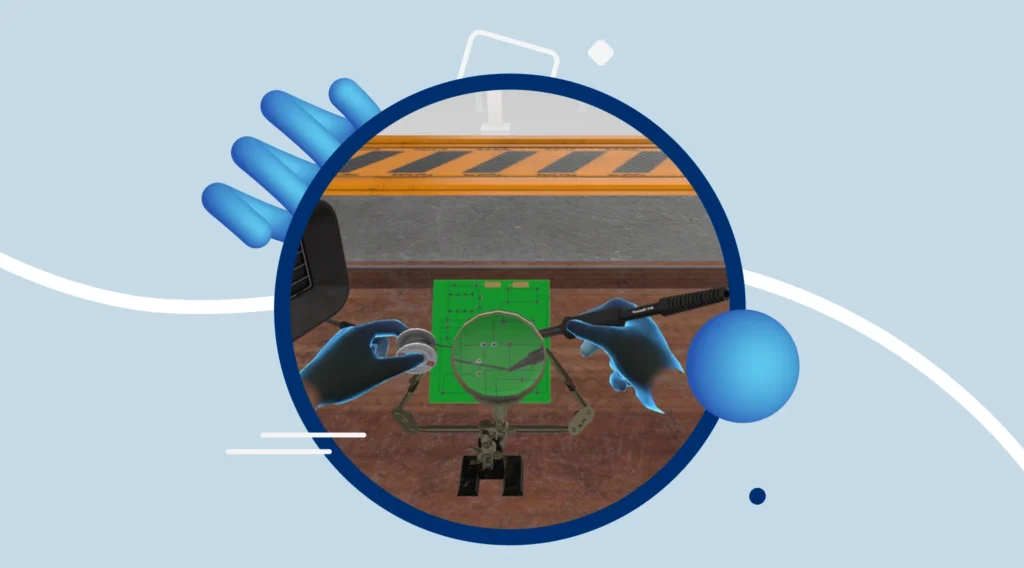
VR Manufacturing/Construction Sims Beat Chat GPT
Playing Transfr manufacturing/construction sims led to significantly better real-world performance than studying a Chat GPT-generated webpage.

Implementation of VR into automotive training classes at Texas State Technical College (TSTC) is associated with the marked increase in the incidence of “A” grades in 2022 vs 2021.

Playing Transfr manufacturing/construction sims led to significantly better real-world performance than studying a Chat GPT-generated webpage.
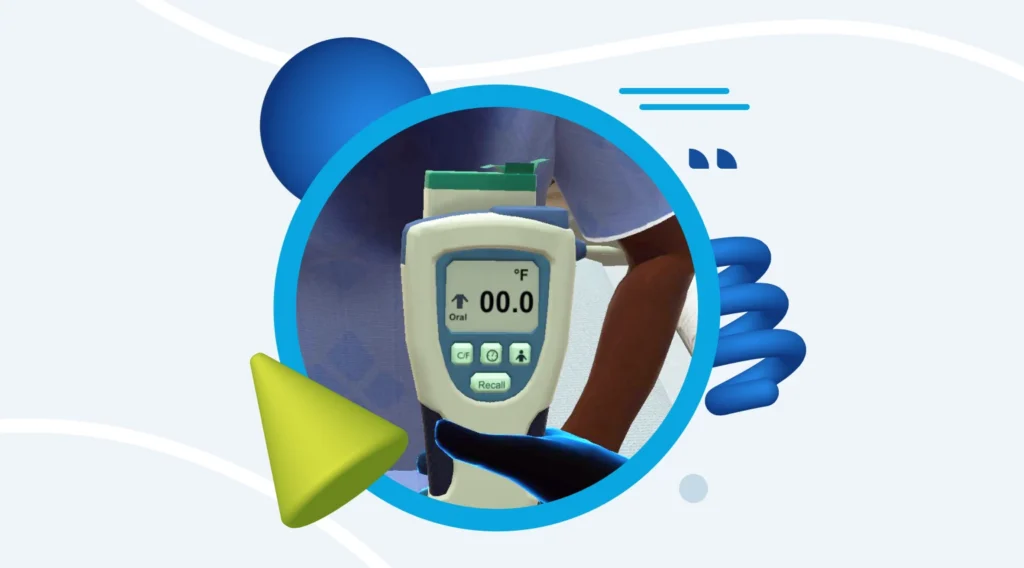

In a health sciences training efficacy study, VR learners showed higher overall average post-test scores and higher average learning gains.
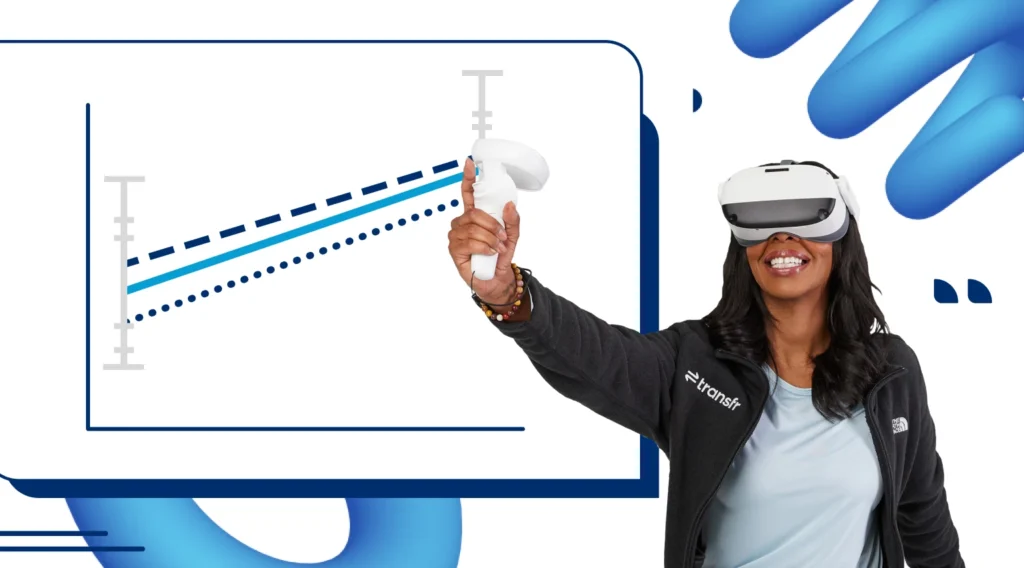

In a study to determine the efficacy of VR depending on the learner’s learning style, participants showed greater learning gain from sim play vs watching, regardless of learning style.

In an anonymous survey, middle schooler reactions to Transfr’s Career Exploration 2.0 sims were strongly positive.

In collaboration with Workforce Solutions of West Central Texas (WSWCT) and Houston, TX-based TRIO Electric…

Transfr conducted comparison studies to measure learning gains made using VR healthcare sims vs slides.

In a study to determine efficacy of VR diesel sims vs a webpage with video content, the VR group showed significantly better learning gains.

In 2023, Transfr conducted research to compare off-task thinking (OTT) in VR training simulations versus other learning scenarios.